- geostrophic scale
- A scale expressed on transparent material and placed across the isobars to measure the geostrophic wind. See also geostrophic wind speed.
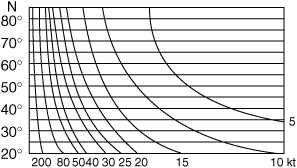 Geostrophic wind scale for use with one standard parallel at 60°N.
Geostrophic wind scale for use with one standard parallel at 60°N.
Aviation dictionary. 2014.

Aviation dictionary. 2014.
Geostrophic wind — The geostrophic wind is the theoretical wind that would result from an exact balance between the Coriolis force and the pressure gradient force. This condition is called geostrophic balance. The geostrophic wind is directed parallel to isobars… … Wikipedia
geostrophic motion — ▪ atmospheric science fluid flow in a direction parallel to lines of equal pressure (isobars) in a rotating system, such as the Earth. Such flow is produced by the balance of the Coriolis force (q.v.; caused by the Earth s rotation) and the … Universalium
Synoptic scale meteorology — The synoptic scale in meteorology (also known as large scale or cyclonic scale) is a horizontal length scale of the order of 1000 kilometres (about 620 miles) or more [American Meteorological Society.… … Wikipedia
climate — /kluy mit/, n. 1. the composite or generally prevailing weather conditions of a region, as temperature, air pressure, humidity, precipitation, sunshine, cloudiness, and winds, throughout the year, averaged over a series of years. 2. a region or… … Universalium
Balanced flow — In atmospheric science, balanced flow is an idealisation of atmospheric motion. The idealisation consists in considering the behaviour of one isolated parcel of air having constant density, its motion on a horizontal plane subject to selected… … Wikipedia
Wind — For other uses, see Wind (disambiguation). Wind, from the … Wikipedia
Coriolis effect — For the psychophysical perception effect, see Coriolis effect (perception). Classical mechanics Newton s Second Law … Wikipedia
Atmospheric model — A 96 hour forecast of 850 mbar geopotential height and temperature from the Global Forecast System An atmospheric model is a mathematical model constructed around the full set of primitive dynamical equations which govern atmospheric motions. It… … Wikipedia
hydrologic sciences — Introduction the fields of study concerned with the waters of the Earth. Included are the sciences of hydrology, oceanography, limnology, and glaciology. In its widest sense hydrology encompasses the study of the occurrence, the… … Universalium
Ocean dynamics — define and describe the motion of water within the oceans. Ocean temperature and motion fields can be separated into three distinct layers: mixed (surface) layer, upper ocean (above the thermocline), and deep ocean. Ocean dynamics has… … Wikipedia